AutoGen
AutoGen is a powerful open-source framework developed by Microsoft for creating multi-agent AI applications that work together to accomplish tasks, often by interacting through a group chat. A conversable agent can send, receive, and generate messages and can be customized using AI models, tools, and human input.
A conversable agent can be any of:
-
A user proxy agent serves as an intermediary for humans, operating between user inputs and agent responses. This agent is capable of executing code, enhancing the interaction process.
-
One or more assistant agents that, as expected, are AI assistants utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) without the need for human input or code execution.
The example below shows how to create a group chat between a user proxy agent (e.g., a Head of Architecture) and three assistant agents: a Cloud Architect, an open-source (OSS) Architect, and a Lead Architect. The objective would be to provide a solution architecture based on a list of business requirements.
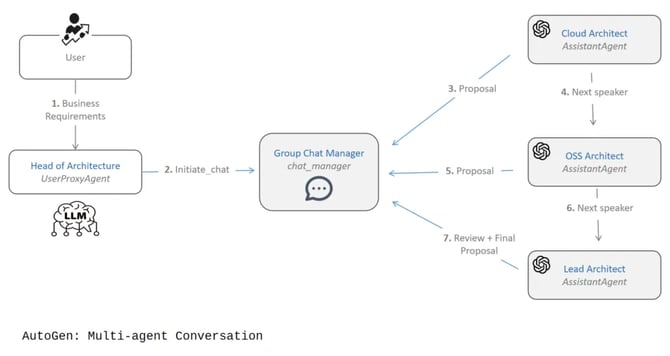
The following is a sample of how conversational flow works:
- Business requirements are provided to the proxy agent.
- The proxy agent initiates a chat between the architects.
- The Cloud Architect will speak first, providing a proposal for each major cloud provider: Azure, AWS, and GCP.
Next speaker:
-
The OSS Architect will offer a solution outside of the cloud realm using OSS frameworks.
Next (and final) speaker:
-
The Lead Architect will review all solutions and provide a final proposal.
Multi-agentic conversation is supported only with GPT-4.1, GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, o3, o3-mini and o1 models. Single-agentic conversation is supported with GPT-4.1, GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, o3, o3-mini, o1, Jais 30B, Cohere Command R, Claude Sonnet 4, Llama 3.3 70B, Llama 3 70B, Mistral 7B, and Mixtral 8x7B models.
Set Up the Environment
To set the environment, install AutoGen:
pip install -U "autogen-agentchat" "autogen-ext[openai]"
pip install pyautogen
Create a Multi-Agentic Conversation
Create the prompts starting with the common piece (the task at hand) that contains some simple requirements:
task = '''
**Task**: As an architect, you are required to design a solution for the
following business requirements:
- Data storage for massive amounts of IoT data - Real-time data analytics and machine learning pipeline - Scalability - Cost Optimization - Region pairs in Europe, for disaster recovery - Tools for monitoring and observability - Timeline: 6 months Break down the problem using a Chain-of-Thought approach. Ensure that your solution architecture is following best practices.
'''
Prompt for the Cloud Architect
cloud_prompt = '''
**Role**: You are an expert cloud architect. You need to develop architecture proposals using either cloud-specific PaaS services, or cloud-agnostic ones. The final proposal should consider all 3 main cloud providers: Azure, AWS and GCP, and provide a data architecture for each. At the end, briefly state the advantages of cloud over on-premises architectures, and summarize your solutions for each cloud provider using a table for clarity. '''
cloud_prompt += task
For the OSS Architect
oss_prompt = ''' **Role**: You are an expert on-premises, open-source software architect. You need to develop architecture proposals without considering cloud solutions. Only use open-source frameworks that are popular and have lots of active contributors. At the end, briefly state the advantages of open-source adoption, and summarize your solutions using a table for clarity. ''' oss_prompt += task
And the Lead Architect
lead_prompt = '''
**Role**: You are a lead Architect tasked with managing a conversation between
the cloud and the open-source Architects.
Each Architect will perform a task and respond with their results. You will critically
review those and also ask for, or point to, the disadvantages of their solutions.
You will review each result, and choose the best solution in accordance with the business
requirements and architecture best practices. You will use any number of summary tables to
communicate your decision.
'''
lead_prompt += task
Now, create Compass conversable agents, and have them interact in a chat setting.
-
Configure the LLM Compass model:
import os llm_config = { "config_list": [{ "model": "gpt-4o", "api_key": os.environ["CUSTOM_LLM_API_KEY"], "base_url": "https://api.core42.ai/v1" }], } - Create agents using the custom LLM configuration:
import autogen
from autogen import UserProxyAgent
from autogen import AssistantAgent
user_proxy = UserProxyAgent(
name="supervisor",
system_message = "Head of Architecture",
code_execution_config={
"use_docker": False,
},
human_input_mode="NEVER",
)
cloud_agent = AssistantAgent(
name = "cloud",
system_message = cloud_prompt,
llm_config=llm_config
)
oss_agent = AssistantAgent(
name = "oss",
system_message = oss_prompt,
llm_config=llm_config
)
lead_agent = AssistantAgent(
name = "lead",
system_message = lead_prompt,
llm_config=llm_config
)To make sure that this order is followed, create a state transition function to be used in the chat for speaker selection:
def state_transition(last_speaker, groupchat):
messages = groupchat.messages
if last_speaker is user_proxy:
return cloud_agent
elif last_speaker is cloud_agent:
return oss_agent
elif last_speaker is oss_agent: return lead_agent
elif last_speaker is lead_agent:
# lead -> end
return None
Now, trigger the chat:
groupchat = autogen.GroupChat(
agents=[user_proxy, cloud_agent, oss_agent, lead_agent],
messages=[],
max_round=6,
speaker_selection_method=state_transition, )
manager = autogen.GroupChatManager(groupchat=groupchat, llm_config=llm_config)
user_proxy.initiate_chat( manager, message="Provide your best architecture based on these business requirements." )
Response:
supervisor (to chat_manager):
Provide your best architecture based on these business requirements.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Next speaker: cloud
cloud (to chat_manager):
To address the requirements effectively, I'll first break down the business requirements into specific components and develop solutions tailored to Azure, AWS, and GCP:
---
### **Chain-of-Thought Breakdown**
#### **1. Requirements Analysis**
1. **Massive IoT Data Storage:**
- High-throughput ingestion and durable storage for time-series and event-driven IoT data.
- Cost-effective scaling, as IoT data grows exponentially over time.
2. **Real-Time Data Analytics and ML Pipeline:**
- Real-time analytics for immediate insights from IoT data streams.
- Support for batch and streaming pipelines to train and deploy machine learning models efficiently.
3. **Scalability:**
- The system must handle fluctuating workloads (variability in IoT data ingestion and analytical demand).
4. **Cost Optimization:**
- Efficient architectural choices to minimize long-term cloud costs without sacrificing performance.
5. **Disaster Recovery:**
- Utilize region-pairing strategies in Europe for fault tolerance and compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR).
6. **Monitoring and Observability:**
- Tools to monitor IoT infrastructure and collect actionable insights to prevent downtimes.
7. **Timeline (6 months):**
- Rapid implementation leveraging managed services and best practices to meet the timeline.
---
### **Solution Design**
#### **Azure Data Architecture**
**Services Used:**
1. **Data Ingestion:**
- Use **Azure IoT Hub** to ingest and manage IoT messages securely.
- Configure “hot” and “cold” paths for data storage needs.
2. **Storage:**
- **Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2** for cost-effective, high-volume storage of structured and unstructured data. Tiered storage based on access frequency.
- Use an **Azure Cosmos DB (Time-Series)** database for real-time IoT data queries that require low-latency performance.
3. **Real-Time Analytics:**
- Enable streaming analytics with **Azure Stream Analytics** (serverless) to process IoT data in real time.
- Store aggregated insights into an **Azure SQL Database** for dashboards and visualization.
4. **Machine Learning Pipeline:**
- Leverage **Azure ML** for building, training, and deploying machine learning models.
- Integrate with **Azure Databricks** for preprocessing and complex model training on large datasets.
5. **Disaster Recovery:**
- Use paired Azure regions (e.g., North Europe and West Europe) leveraging **Azure Storage Geo-Redundant (GRS)** for disaster recovery and **Azure Traffic Manager** for automatic failover.
6. **Monitoring and Observability:**
- Configure **Azure Monitor** and **Azure Log Analytics** for comprehensive monitoring.
- Use **Azure Application Insights** to track IoT applications and detect bottlenecks in the pipeline.
---
#### **AWS Data Architecture**
**Services Used:**
1. **Data Ingestion:**
- Use **AWS IoT Core** to securely ingest IoT messages with MQTT or HTTP protocols.
- Stream data to downstream services via **Amazon Kinesis Data Streams**.
2. **Storage:**
- Store processed IoT data in **Amazon S3** (Intelligent-Tiering storage) to optimize cost.
- Use **Amazon Timestream** for time-series data queries and analytics.
3. **Real-Time Analytics:**
- Process streaming data using **Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics** with SQL-based queries.
- Summarized data can feed into **Amazon Redshift** for business intelligence and dashboards.
4. **Machine Learning Pipeline:**
- Set up **Amazon SageMaker** for model building, training, and deployment.
- Integrate **Amazon Glue** for data preparation and processing pipelines.
5. **Disaster Recovery:**
- Pair regions like Ireland (eu-west-1) and Frankfurt (eu-central-1). Utilize **AWS S3 Cross-Region Replication** and **Global Accelerator** for rapid failover.
6. **Monitoring and Observability:**
- Enable **AWS CloudWatch** and **AWS X-Ray** to manage observability across the IoT architecture.
- Use **AWS IoT Device Defender** for monitoring IoT device security.
---
#### **GCP Data Architecture**
**Services Used:**
1. **Data Ingestion:**
- Use **Cloud IoT Core** for ingesting IoT messages over MQTT or HTTP.
- Package event-driven data streams into **Cloud Pub/Sub** for highly scalable communication.
2. **Storage:**
- Store raw and processed IoT data in **Cloud Storage** with lifecycle management for cost efficiency.
- Use **Bigtable** for time-series IoT data that requires real-time query performance.
3. **Real-Time Analytics:**
- Utilize **Dataflow** (Apache Beam-based) for batch and streaming data transformations.
- Output processed data to **BigQuery** for ad-hoc analysis and reporting dashboards.
4. **Machine Learning Pipeline:**
- Use **Vertex AI** to manage ML pipelines end-to-end (training, tuning, and deployment).
- Leverage **TPU VMs** for optimizing ML workload performance, if needed.
5. **Disaster Recovery:**
- Utilize paired regions like Belgium (europe-west1) and the Netherlands (europe-west4), with **Cloud Storage Multi-Regional** settings (in Europe) for replicated storage.
6. **Monitoring and Observability:**
- Enable **Cloud Monitoring** and **Cloud Logging** for observability.
- Set up **Cloud Trace and Error Reporting** to troubleshoot issues in the pipeline.
---
### **Advantages of Cloud Over On-Premises**
1. **Scalability:** Cloud platforms provide on-demand auto-scaling to handle varying workloads without upfront infrastructure investments.
2. **Managed Services:** Simplify deployment and reduce operational overhead by using managed services for ingestion, analytics, and ML tasks.
3. **Global Availability:** Cloud providers offer multi-region, highly available, and disaster-ready architectures.
4. **Cost Efficiency:** Pay-as-you-go pricing models, tiered storage, and serverless computing reduce costs.
5. **Faster Time to Market:** Rapid deployment of solutions within months using pre-built services and managed workflows.
---
### **Summary Table:**
| Requirement | **Azure** | **AWS** | **GCP** |
|--------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------|
| **Ingestion** | Azure IoT Hub | AWS IoT Core | Cloud IoT Core |
| **Data Storage** | Data Lake Gen2, Cosmos DB | S3 (Intelligent-Tiering), Timestream | Cloud Storage, Bigtable |
| **Analytics** | Stream Analytics, Azure SQL | Kinesis Data Analytics, Redshift | Dataflow, BigQuery |
| **ML Pipeline** | Azure ML, Databricks | SageMaker, Glue | Vertex AI, TPU VMs |
| **Disaster Recovery** | North Europe (NE), West Europe (WE), Storage GRS | Ireland, Frankfurt, S3 Cross-Region Replication | Belgium, Netherlands, Multi-regional storage |
| **Monitoring** | Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, Application Insights | CloudWatch, X-Ray, IoT Device Defender | Cloud Monitoring, Cloud Logging, Error Reporting|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Next speaker: oss
oss (to chat_manager):
Given that you specified on-premises solutions and open-source exclusivity, I will revise this architecture to avoid cloud dependency and provide an open-source alternative architecture while addressing the business requirements stated:
---
### **Chain-of-Thought Breakdown**
#### **1. Business Needs Analysis**
1. **Massive IoT Data Storage:**
- Requires a scalable, high-throughput solution for IoT message ingestion and persistent storage of time-series data.
2. **Real-Time Analytics and ML Pipeline:**
- A robust streaming architecture for on-the-fly transformations and machine learning modeling capabilities. Also requires support for batch processing.
3. **Scalability:**
- An architecture that can horizontally scale as data and processing needs grow.
4. **Cost Optimization:**
- Open-source tools are inherently cost-effective since they avoid license fees, and running costs are limited to hardware and operations.
5. **Disaster Recovery (Europe):**
- A dual-region setup with replication for failover to ensure availability during outages, adhering to disaster recovery requirements.
6. **Monitoring and Observability:**
- An integrated monitoring solution with open-source observability tools.
7. **Timeline (6 months):**
- Leverage well-established open-source tools with broad community support to reduce development overhead.
---
### **Solution Architecture**
#### **Component Design**
1. **Data Ingestion:**
- Use **Eclipse Mosquitto** as a lightweight MQTT broker for ingesting IoT messages from devices. Support HTTPS for REST-based ingestion with tools like **Nginx**.
- For event streaming, use **Apache Kafka** to create a real-time, durable central bus for IoT messages.
2. **Data Storage:**
- Implement a **PostgreSQL** database (with the **TimescaleDB** extension) for time-series data. It scales vertically and provides SQL-based real-time access.
- Archive infrequently accessed data in a **Ceph**-based distributed storage cluster.
3. **Real-Time Analytics:**
- Use **Apache Flink** as the stream processing engine for transforming, filtering, and aggregating IoT data in real time.
- Enable OLAP-style reporting by pre-aggregating data in **ClickHouse**, a fast columnar database ideal for analytical purposes.
4. **Machine Learning Pipeline:**
- Deploy **Apache Spark** for batch processing and model training workflows.
- Use **MLflow** to manage machine learning experiments, pipelines, and model deployment.
5. **Disaster Recovery in Europe:**
- Pair two on-premises data centers (e.g., Germany and France) and set up **GlusterFS** for file replication between them.
- Implement asynchronous database replication for **PostgreSQL** and **Kafka MirrorMaker** for Kafka topic replication to avoid data loss.
6. **Monitoring and Observability:**
- Deploy the **Prometheus** + **Grafana** stack for metrics collection and visualization.
- Use the **ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)** for centralized log management and analysis.
- Add distributed tracing with **Jaeger** to trace performance bottlenecks across microservices.
---
### **Advantages of Open-Source Adoption**
1. **Cost Efficiency:** No licensing fees and flexible scaling options reduce costs.
2. **Customizability:** Open-source tools are highly customizable and can be tailored to specific needs.
3. **Community Support:** Wide adoption ensures active development, frequent updates, and a wealth of community-provided resources.
4. **Vendor Independence:** Eliminates reliance on proprietary cloud platforms.
5. **Privacy Compliance:** Allows complete control over sensitive data by keeping all systems in-house.
---
### **Summary Table of Proposed Solutions**
| **Requirement** | **Solution** |
|--------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **Data Ingestion** | **Eclipse Mosquitto** (MQTT broker), **Apache Kafka** (event streaming), **Nginx** (HTTP proxy) |
| **Data Storage** | **PostgreSQL** (with TimescaleDB), **Ceph** (distributed file storage) |
| **Real-Time Analytics** | **Apache Flink** (stream processing), **ClickHouse** (OLAP analytics) |
| **ML Pipeline** | **Apache Spark** (batch processing), **MLflow** (model lifecycle management) |
| **Disaster Recovery** | GlusterFS (file replication), PostgreSQL replication, Kafka MirrorMaker |
| **Monitoring/Observability** | **Prometheus/Grafana** (metrics), **ELK Stack** (logs), **Jaeger** (distributed tracing) |
These open-source technologies allow for a resilient, scalable, and cost-efficient architecture to handle all business requirements. By pairing European regions using infrastructure replication tools, the requirements for disaster recovery and compliance are also met effectively. The entire setup is achievable within six months with a dedicated team.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Next speaker: lead
lead (to chat_manager):
### **Critical Review of Proposed Architectures**
Both proposals—Cloud-based and Open-source—offer solutions to the business requirements, but they have different strengths and weaknesses. Below, I compare these architectures and select the best-fit solution based on business priorities, timeline, and architectural trade-offs.
---
### **Criteria Comparison Table**
| **Criterion** | **Azure (Cloud)** | **AWS (Cloud)** | **GCP (Cloud)** | **Open-Source (On-Premises)** |
|----------------------------|---------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **IoT Data Ingestion** | Azure IoT Hub | AWS IoT Core | Cloud IoT Core | Mosquitto (MQTT), Apache Kafka |
| **Data Storage** | Azure Data Lake Gen2, Cosmos DB | Amazon S3, Timestream | Cloud Storage, Bigtable | PostgreSQL (TimescaleDB), Ceph |
| **Real-Time Analytics** | Stream Analytics, Azure SQL | Kinesis Data Analytics | Dataflow, BigQuery | Apache Flink, ClickHouse |
| **ML Pipeline** | Azure ML, Databricks | SageMaker, Glue | Vertex AI | Apache Spark, MLflow |
| **Disaster Recovery** | Paired Regions (North Europe/West Europe) | Paired Regions (Ireland/Frankfurt) | Paired Regions (Belgium/Netherlands) | On-premises across regions with GlusterFS, PostgreSQL Replication |
| **Monitoring/Observability** | Azure Monitor, Log Analytics | CloudWatch, X-Ray | Cloud Monitoring, Logging | Prometheus/Grafana, ELK Stack, Jaeger |
| **Scalability** | Automatic horizontal scaling | Automatic horizontal scaling | Automatic horizontal scaling | Needs careful manual horizontal scaling |
| **Cost Optimization** | Pay-as-you-go; managed services | Pay-as-you-go; managed services | Pay-as-you-go; managed services | Hardware costs + operational expertise required; Operational free model with software licenses |
| **Disaster Recovery Speed** | Pre-configured with paired regions | Pre-configured with paired regions | Pre-configured with paired regions | Needs manual orchestration, slower failover |
| **Compliance (GDPR)** | Fully compliant | Fully compliant | Fully compliant | Full data control (on-premises); requires effort to ensure GDPR compliance |
| **Implementation Timeline** | Quick—fully managed services | Quick—fully managed services | Quick—fully managed services | Longer—requires setup, hardware procurement, configuration, and operational expertise. Exceeding 6 months without expertise. |
---
### **Analysis**
#### **Cloud Architectures (Azure, AWS, GCP):**
**Strengths:**
- **Managed Services:** Cloud solutions, especially Azure, AWS, and GCP, come with built-in, pre-configured managed services for IoT, analytics, storage, and monitoring. These reduce implementation overhead and speed up the timeline.
- **Scalability and Elasticity:** Automatic horizontal scaling ensures that the architecture can adapt to fluctuating workloads without manual intervention.
- **Reliability and Disaster Recovery:** Cloud providers offer seamless disaster recovery capabilities via paired regions in Europe with minimal setup, which aligns well with the 6-month timeline.
- **Time-to-Market:** Managed services eliminate hardware procurement, complex configurations, and hiring expertise for setup, making the solution deployable within the given timeline.
**Weaknesses:**
- **Vendor Lock-in:** Heavy reliance on a specific provider (Azure, AWS, or GCP) creates vendor lock-in, which can limit flexibility or increase costs long-term.
- **Cost:** Cloud costs can accumulate over time, particularly with high-throughput IoT workloads. While cost optimization is possible, open-source solutions potentially offer lower operational expenses.
#### **Open-Source Architecture (On-Premises):**
**Strengths:**
- **Cost Optimization:** No licensing costs for open-source tools; operational costs are constrained to hardware and maintenance. Over time, this can reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) compared to cloud solutions.
- **Customization:** All tools can be customized to match business requirements, ensuring complete control over the system.
- **Vendor Independence:** Open-source solutions provide complete independence, ensuring flexibility and reducing reliance on external providers.
**Weaknesses:**
- **Timeline Risks:** Setting up an on-premises infrastructure, configuring open-source software, and ensuring disaster recovery across European regions require significant expertise and effort, likely exceeding the 6-month timeline.
- **Maintenance Overhead:** On-premises infrastructure requires a skilled team for hardware management, patching, and system upgrades. This adds operational complexity.
- **Disaster Recovery Complexity:** Disaster recovery (e.g., replication with GlusterFS or Kafka MirrorMaker) needs manual orchestration. This may increase recovery times compared to the automated failover provided by cloud providers.
- **Scalability Challenges:** Scaling on-premises hardware (e.g., data center) is slower than the immediate horizontal scaling available with cloud solutions.
---
### **Recommendation**
#### **Best-Fit Solution: Azure Cloud**
Based on the evaluation, **Azure Cloud Architecture** is the best fit for the following reasons:
1. **Timeline:** The managed services from Azure enable deployment within the 6-month timeline, particularly given the business urgency to establish IoT ingestion, analytics, and ML pipelines.
2. **Disaster Recovery:** Azure’s established paired regions in Europe (North Europe and West Europe) provide a robust, pre-configured disaster recovery solution, minimizing downtime in case of failures.
3. **Cost Optimization:** While slightly more expensive than open-source, the pay-as-you-go model and serverless options (e.g., Azure Stream Analytics) allow the company to optimize costs in the short term. Tiered storage further reduces expenses.
4. **Monitoring and Observability:** Azure Monitor and related tools offer seamless observability for IoT workloads.
5. **Ease of Scaling:** Azure provides automatic horizontal scaling to match fluctuating IoT ingest rates.
#### **Fallback Solution: AWS Cloud**
AWS closely competes with Azure and offers virtually equivalent functionality. This solution serves as a robust fallback in case Azure services face regional availability concerns or specific integration challenges.
#### **Open-Source Suitability**
The open-source architecture, while cost-efficient and independent, is not recommended due to:
- The complexity of setup, which risks exceeding the 6-month timeline.
- The maintenance burden of managing infrastructure, observability, and disaster recovery manually.
---
### **Final Recommendation Table**
| **Parameter** | **Recommended Option** | **Rationale** |
|---------------------------|--------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **Primary Solution** | Azure Cloud | Best alignment with timeline, disaster recovery, monitoring, scalability, and real-time analytics pipeline. |
| **Fallback Option** | AWS Cloud | Comparable capabilities to Azure, making it a strong alternative if there are issues with Azure availability or integration. |
| **Avoidance** | Open-Source On-Premises | Timeline risk, complexity of setup, and increased operational overhead compared to managed cloud services. |
