Chat Completion
When given a list of messages, the models return a response.
Create a Chat Completion
Creates a completion for the chat message.
Azure OpenAI
Request
POST https://api.core42.ai/openai/deployments/{deployment-id}/chat/completions
| Name | In | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| deployment-id | path | true | string |
Model to use for this request. Available models are gpt-5, gpt-5-mini, gpt-4.1, gpt-4o, gpt-4o-audio-preview, gpt-4o-mini, o3, o3-mini, o4-mini-2025-04-16, o1, jais-30b, Llama-3.3-70B, llama3-70b, mixtral-8x7b, mistral-7b, gpt-oss-120b-crerebras, gpt-oss-120b-core42, gpt-oss-120b-azure, gpt-oss-120b-core42-amd, gpt-oss-20b-core42-amd, gpt-oss-120b-qualcomm, gpt-oss-20b-qualcomm, gpt-oss-20b-core42, claude-sonnet-4, qwen3-14b, command-a-03-2025, and cohere-command-r-08-2024. Note: GPT-4o model supports image and text inputs and generates text output. Note: GPT-4o supports the following model versions:
|
| api-version | query | true | string | For the available API versions, refer to Microsoft Azure documentation. |
OpenAI
Request
POST https://api.core42.ai/v1/chat/completions
Request Parameters
|
Name |
Required |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
model |
true |
string |
Model to use for this request. Available models are gpt-4.1, gpt-4o, gpt-4o-audio-preview, gpt-5, gpt-5-mini, gpt-4o-mini, o3, o3-mini, o4-mini-2025-04-16, o1, jais-30b, Llama-3.3-70B, llama3-70b, mixtral-8x7b, mistral-7b, gpt-oss-120b-crerebras, gpt-oss-120b-core42, gpt-oss-120b-azure, gpt-oss-120b-core42-amd, gpt-oss-20b-core42-amd, gpt-oss-120b-qualcomm, gpt-oss-20b-qualcomm, gpt-oss-20b-core42, claude-sonnet-4, qwen3-14b, command-a-03-2025, and cohere-command-r-08-2024. Note: GPT-4o model supports image and text inputs and generates text output. GPT-4o mini supports text input and text outputs. Note: GPT-4o supports the following model versions:
|
|
messages[].role |
true |
string |
The message’s author role. |
|
messages[].content |
true |
string |
Contents of the message. |
|
messages[].name |
false |
string |
User’s name in a multi-user chat. |
|
audio |
false |
object or null |
Parameters for audio output. Required when audio output is requested with modalities: ["audio"]. |
|
audio[].format |
true |
string |
Specifies the output audio format. Supported formats are wav, mp3, flac, opus, or pcm16. When using gpt-4o-audio-preview and stream is set to true, the only supported audio format is pcm16. |
|
audio[].voice |
true |
string |
The voice the model uses to respond. Supported voices are alloy, echo, |
|
modalities |
false |
array or null |
Output types you would like the model to generate. The default is
The To request that this model generate both text and audio responses, use
|
|
temperature |
false |
number |
The temperature controls randomness. The range is from 0 to 2. Lowering results in less random completion. If the value approaches 0, the model tends to produce more predictable and deterministic responses. If the value approaches to 2, it produces more randomness, resulting in responses that are less predictable and more diverse. |
|
top_p |
false |
number |
An alternative to the temperature parameter, also called nucleus sampling, is where the model considers the results of the tokens with top_p probability mass. 0.1 means only the tokens comprising the top 10% probability mass are considered. It is recommended to alter this or the temperature, but not both. Setting top_p to 0.9 increases the selection of words, allowing the model to consider a wider range of options. This results in more varied and original responses, potentially leading to more imaginative and engaging suggestions for the adventure book title. |
|
n |
false |
integer |
Number of chat completion choices to generate for each input message. The user will be charged based on the number of generated tokens across all the choices. Keep n as 1 to minimize cost. |
|
stream |
false |
boolean |
Facilitates the generation of responses in a streaming fashion. The default value is set as false. When set to false, partial message deltas will be sent, like in ChatGPT. Tokens will be sent as data-only server-sent events as they become available, with the stream terminated by a data: [DONE] message. When streaming is enabled, messages are sent in real-time and in a partial manner. The server sends chunks of data as they become available, and the client receives these incrementally. This streaming of data continues until the server decides to close the connection or the complete response has been sent. |
|
stop |
false |
string, array |
Up to four sequences where the API will stop generating further tokens. |
|
max_tokens |
false |
integer |
The maximum number of tokens that can be generated during the chat completion. The model's context length limits the total length of input tokens and generated tokens. |
|
max_completion_tokens |
false |
integer or null |
The maximum number of tokens that can be generated for a completion, including visible output tokens and reasoning tokens. Note: This parameter applies only to GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, o3, o3-mini, and o1 models. |
|
presence_penalty |
false |
number |
Number between -2.0 and 2.0. Positive values encourage the model to include new tokens based on their appearance in the text so far to talk about new topics. Note: This does not apply to the Jais 30B model. |
|
frequency_penalty |
false |
number |
Allowed values are between -2.0 and 2.0. Positive values discourage the model from repeating the same text, words, or phrases based on their existing frequency. |
|
repitition_penalty |
false |
number |
Set the value to 1.1 to stop repetition of the data. |
|
logit_bias |
false |
object |
Modifies the chances of specified tokens appearing in the completion. Accepts a JSON object that maps tokens (specified by their token ID in the tokenizer) to an associated bias value from -100 to 100. Mathematically, the bias is added to the logits generated by the model prior to sampling. The exact effect will vary per model, but values between -1 and 1 should decrease or increase the likelihood of selection; values like -100 or 100 should result in a ban or exclusive selection of the relevant token. |
|
user |
false |
string |
A unique identifier that represents the user. |
|
safety_identifier |
false |
string |
A stable identifier used to help detect users of your application that may be violating OpenAI's usage policies. The IDs should be a string that uniquely identifies each user. Compass recommends hashing their username or email address to avoid sending us any identifying information. Learn more about safety_identifier. |
|
prompt_cache_key |
false |
string |
Used by OpenAI to cache responses for similar requests to optimize your cache hit rates. Replaces the user field. Learn more about prompt_cache_key. |
|
store |
false |
boolean or null |
Whether or not to store the output of this chat completion request for use in our model distillation or evals products. The default value is false Supports text and image inputs. Note: Image inputs over 8MB in size will be dropped. |
|
service_tier |
false |
string or null |
Specifies the processing type used for serving the request.
When the service_tier parameter is set, the response body will include the service_tier value based on the processing mode actually used to serve the request. This response value may be different from the value set in the parameter. |
|
top_logprobs |
false |
integer or null |
An integer between 0 and 20 specifying the number of most likely tokens to return at each token position, each with an associated log probability. logprobs must be set to true if this parameter is used. |
|
top_k |
nullable=true |
integer |
Number of highest probability vocabulary tokens to keep for top-k-filtering. The default value is null. |
|
do_sample |
nullable=true |
boolean |
If set to True, this parameter enables decoding strategies such as multinomial sampling, beam-search multinomial sampling, top-k sampling, and top-p sampling. All these strategies select the next token from the probability distribution over the entire vocabulary with various strategy-specific adjustments. |
|
max_seconds |
nullable=true |
integer, int32 |
Signed 32-bit integers (commonly used integer type). |
|
num_beams |
nullable=true |
integer, int32 |
By specifying a number of beams higher than 1, you are effectively switching from greedy search to beam search. |
|
ts |
false |
string |
Timestamp of the request. For example, 2024-03-18T05:40:18.264Z |
|
tools |
false |
array |
A list of tools the model can call. As of now, only functions are supported as a tool. The supported models are GPT-4.1, GPT-4o, GPT-4o Audio, o3-mini, and o1 models. For more information, see tools parameter. The tool has type and function properties. |
|
tools[].type |
true |
string |
Defines the tool type. Supports only function as of now. |
|
tools[].function |
true |
object |
The function contains description, name, and parameters fields to be provided. |
|
tools[].function[].description |
false |
string |
A description of what the function does, used by the model to choose when and how to call the function. |
|
tools[].function[].name |
true |
string |
The name of the function to be called. Must be a-z, A-Z, 0-9, or contain underscores and dashes, with a maximum length of 64. |
|
tools[].function[].parameters |
true |
object |
The parameters the functions accept are described as a JSON Schema object. See the guide for examples, and the JSON Schema reference for documentation about the format. Omitting parameters defines a function with an empty parameter list. |
|
tools[].function[].strict |
false |
boolean or null |
Whether to enable strict schema adherence when generating the function call. If set to true, the model will follow the exact schema defined in the parameters field. Only a subset of JSON Schema is supported when strict is true. |
|
tool_choice |
false |
string |
Controls if any tool is called by the model. The available values are none, auto, and required. If set to none, the model will not call any tool and generate a message. This is the default value when no tool is present. If set to auto, the model can pick between generating a message or calling one or more tools. If set to required, the model must call one or more tools by specifying a particular tool with the following format. Default when tools are present. |
|
verbosity |
false |
string or null |
Constrains the verbosity of the model's response. Lower values will result in more concise responses, while higher values will result in more verbose responses. Currently supported values are low, medium, and high. |
|
safe_prompt |
false |
boolean |
Specifies whether to inject a safety prompt before all conversations. Note: This parameter is only available for Mistral 7B model. |
|
reasoning_effort |
false |
string or null |
Constrains effort on reasoning for reasoning models. Currently supported values are Reducing reasoning effort can result in faster responses and fewer tokens used on reasoning in a response. Note: This parameter is available only with GPT-5, GPT-5 mini, gpt-oss-120b, gpt-oss-20b, o1, o3, o3-mini, and o4-mini models. |
|
random_seed |
nullable=true |
integer |
Seed to use for random sampling. |
|
thinking
|
false |
object |
Configuration for enabling extended thinking. When enabled, responses include thinking content blocks that show Claude's thought process before the final answer. Requires a minimum budget of 1,024 tokens and counts towards your max_tokens limit. See extended thinking for details. Note: This parameter is available only with the Claude Sonnet 4, and Qwen 3 14B models. |
|
thinking_budget |
false |
integer |
Specifies the maximum length of the thinking process. This parameter is applicable only when
Note: This parameter is available only with the Qwen 3 14B model. |
|
documents |
false |
list of strings or object |
A list of relevant documents that the model can cite to generate a more accurate reply. Each document is either a string or a document object with content and metadata. Note: This parameter is available only with the Cohere Command R model. |
|
documents[].data |
true |
object |
A relevant document that the model can cite to generate a more accurate reply. Each document is a string or a dictionary. Note: This parameter is available only with the Cohere Command R model. |
|
documents[].id |
false |
string |
A unique identifier for this document, which will be referenced in citations. If not provided, an ID will be automatically generated. Note: This parameter is available only with the Cohere Command R model. |
|
citation_options |
false |
object |
Options for controlling citation generation. |
|
mode |
false |
enum |
Defaults to "accurate". Dictates the approach taken to generating citations as part of the RAG flow by allowing the user to specify whether they want "accurate" results, "fast" results, or no results. The default is "fast". Allowed values: FAST, ACCURATE, OFF Note: This parameter is available only with the Cohere Command R model. |
|
response_format |
false |
object |
Configuration for forcing the model output to adhere to the specified format. Supported on Command R models. The model can be forced into outputting JSON objects by setting { "type": "json_object" }. A JSON Schema can be optionally provided to ensure a specific structure. Note: When using { "type": "json_object" } your message should always explicitly instruct the model to generate a JSON (eg: “Generate a JSON …”) . Otherwise, the model may end up getting stuck, generating an infinite stream of characters, and eventually run out of context length. Note: When json_schema is not specified, the generated object can have up to 5 layers of nesting. Limitation: The parameter is not supported when used in combination with the documents or tools parameters. Note: This parameter is available only with the Cohere Command R model. |
|
min_p
|
false |
number |
Dynamic filtering threshold that adapts based on token probabilities. The default value is 0.05. Note: This parameter applies only to Qwen3-Reranker-8B, and Qwen3-14B models. |
stream
The stream parameter facilitates the generation of responses in a streaming fashion, allowing for real-time interaction and continuous output.
When stream = false
Sample Request Format
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"stream": false,
"messages": [{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello"
}]
}
Sample Response Format
Hello How are you Today?
With Streaming Disabled:
- The entire response is generated at once and returned as a single block of text.
- The entire narrative is available immediately, suitable for scenarios where immediate access to the complete response is preferred.
This method is useful when you need the entire generated text for further processing or analysis without waiting for it to be generated incrementally.
When stream=true
Sample Request Format
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"stream": true,
"messages": [{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hi"
}]
}
Sample Response Format

Server: Sends a data chunk, "Hello"
Client: Receives, "Hello"
Server: Sends another data chunk, "how are you?"
Client: Receives, "how are you?"
Server: Sends the final data chunk, "today?"
Client: Receives, "today?"
With streaming enabled:
- In the context of Server-Sent Events (SSE) using EventSource, messages are sent in real-time and in a partial manner. This means that the server sends pieces of data as they become available, and the client receives these pieces incrementally. This streaming of data continues until the server decides to close the connection or the complete response has been sent.
- With a streaming API call, the response is sent back incrementally in chunks via an event stream. In Python, you can iterate over these events with a for loop.
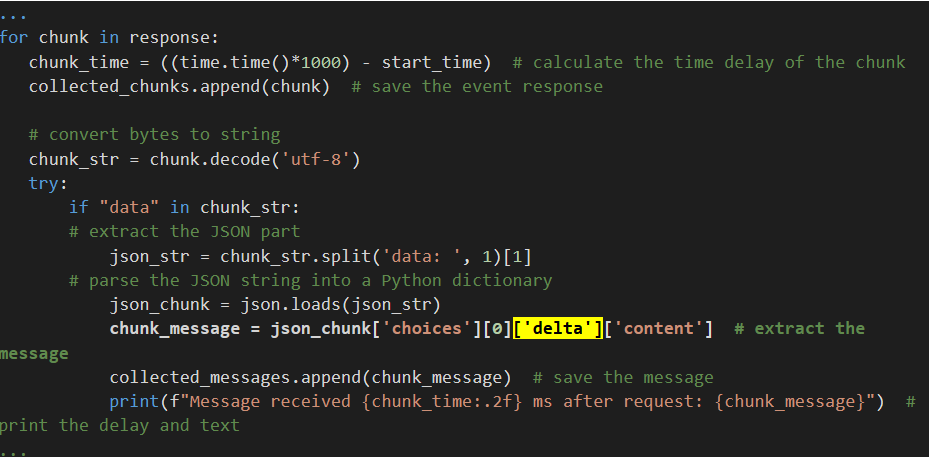
The below example shows the time elapsed for each data chunk:
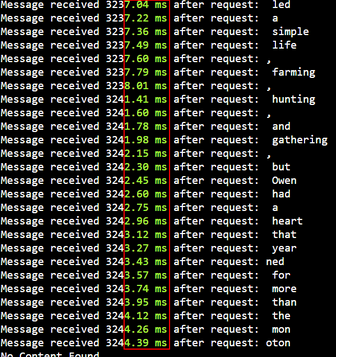
This method is suitable to display text as it's generated, creating a sense of anticipation and engagement.
temperature
The temperature parameter in the Compass API influences the level of randomness in the generated text. It controls how conservative or exploratory the model is when generating responses.
Examples of Request and Responses
1. temperature = 0
Request
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What are the benefits of exercising?"
}
],
"temperature": 0,
"max_tokens": 50
}
Response
"Exercising improves heart health and muscle strength, lowers the chance of chronic diseases, and helps manage weight."
At a temperature of 0, the model selects the most likely words, resulting in a highly predictable and factual response. This is ideal for scenarios where accuracy is paramount, such as providing information on health benefits.
2. temperature = 1
Request
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What are the benefits of exercising?"
}
],
"temperature": 1,
"max_tokens": 50
}
Response
"Exercise is the alchemist turning sweat into a miracle cure, a ritual dancing in the flames of effort and reward."
At a temperature of 1, the model takes more creative liberties and chooses less likely words, resulting in a more imaginative but unpredictable response. This level of temperature encourages the generation of diverse and creative answers, which can be suitable for contexts where engaging the audience with unique perspectives is desired.
top_p
Also known as nucleus sampling, it constrains the probability distribution to the top_p tokens. This helps in maintaining response diversity by limiting the selection of tokens based on their likelihood. Higher values of top_p allow for a wider selection of tokens, potentially leading to more varied responses.
Examples of Request and Responses
1. top_p = 0.5
Request
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Please suggest a title for an adventure book."
}
],
"top_p": 0.5,
"max_tokens": 50
}
Response
"The Enigma of Emerald Island."
With a top_p value of 0.5, the model selects words that collectively represent at least 50% of the total probability distribution. This ensures a diverse range of responses while maintaining coherence.
2. top_p = 0.9
Request
{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Please suggest a title for an adventure book."
}
],
"top_p": 0.9,
"max_tokens": 50
}
Response
"Echoes from the Forgotten Jungle: Chronicles of the Fearless Explorer."
Explanation
Setting top_p to 0.9 expands the selection of words, allowing the model to consider a wider range of options. This results in more varied and original responses, potentially leading to more imaginative and engaging suggestions for the adventure book.
tools
In the below example, a function, get_current_weather is defined and called the model. The model can use this function to retrieve information based on the input location. When a user asks question regarding weather, this is something that model cannot tell because of lack of information, instead, it can detect the available functions to provide this kind of information. So, the model will build input parameters based on user questions and indicate which function needs to be called. Once the function is called as per the model suggestion, the response is returned. The model will eventually be able to answer the user's question regarding the weather. you can do the following with the response:
-
1. Send the user conversation and available functions to the model.
-
2. Based on the model response, call the particular functions.
-
3. Send information for each function call and function response to the model.
from openai import OpenAI
import json
client = OpenAI(
base_url = "https://api.core42.ai/v1",
default_headers={"api-key": "<API_KEY>"},
api_key="XXX"
)
# Example dummy function hard coded to return the same weather
# In production, this could be your backend API or an external API
def get_current_weather(location, unit="fahrenheit"):
"""Get the current weather in a given location"""
if "tokyo" in location.lower():
return json.dumps({"location": "Tokyo", "temperature": "10", "unit": unit})
elif "san francisco" in location.lower():
return json.dumps({"location": "San Francisco", "temperature": "72", "unit": unit})
elif "paris" in location.lower():
return json.dumps({"location": "Paris", "temperature": "22", "unit": unit})
else:
return json.dumps({"location": location, "temperature": "unknown"})
def run_conversation():
# Step 1: send the conversation and available functions to the model
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in San Francisco, Tokyo, and Paris?"}]
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
},
}
]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto", # auto is default, but we'll be explicit
)
response_message = response.choices[0].message
tool_calls = response_message.tool_calls
# Step 2: check if the model wanted to call a function
if tool_calls:
# Step 3: call the function
# Note: the JSON response may not always be valid; be sure to handle errors
available_functions = {
"get_current_weather": get_current_weather,
} # only one function in this example, but you can have multiple
messages.append(response_message) # extend conversation with assistant's reply
# Step 4: send the info for each function call and function response to the model
for tool_call in tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
function_response = function_to_call(
location=function_args.get("location"),
unit=function_args.get("unit"),
)
messages.append(
{
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"role": "tool",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
) # extend conversation with function response
second_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
) # get a new response from the model where it can see the function response
return second_response
print(run_conversation())
